As George W. Bush’s Secretary for Defense Donald Rumsfeld once remarked: “There are things we know that we know. There are known unknowns. That is to say there are things that we now know we don’t know. But there are also unknown unknowns. There are things we do not know we don’t know.”
Getting Rumsfeld’s statement word perfect is challenging, but it nevertheless readily comes to mind when observing and monitoring English local authorities. As long ago as 1960 Parliament passed the Public Bodies (Admission to Meetings) Act - sponsored by a newly-elected back bench MP called Margaret Thatcher - which forced local authorities to hold their meetings in public unless specific exemptions from that rule applied. The detailed rules have been updated from time to time, but the principle remains the same.
What we get under these rules is of course what councils want us to see. To be fair, officer reports seeking a decision – considered by councillors in public session - often contain a wealth of detail, including nuggets that councillors might prefer were not public. Some reports, and most financial ones, require a degree of knowledge or decoding expertise not possessed by most people. So is this enough to enable we, the people, to scrutinise and hold our councils to account?
Let’s look at what is readily available. Council websites are the obvious starting point, though they are usually designed to help people find out what day their bin is emptied rather than reveal background information. Taking Exeter City Council as an example, start with the pages under the “Council and Democracy” heading. This will take you to information about: councillors; agendas, papers and minutes of meetings; plans and policies; financial information including the annual budget and audit reports. Under Council Data, a miscellany of statistics and information on contracts.
The minutes and papers are a good starting point for anyone wanting to research a particular topic or find out what the council has been discussing. Or simply for fishing. There is a facility for searching documents, though the results are at times unhelpful. Time and patience are required, but the investment is often worth it.
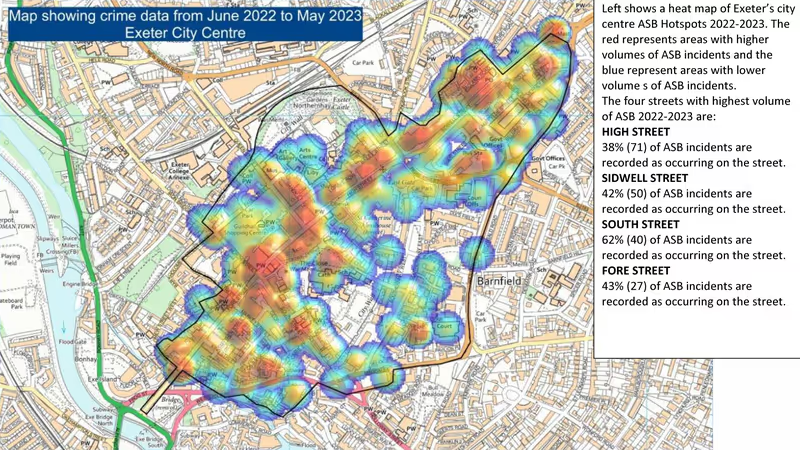
Elsewhere on the website, the most fascinating and useful set of tables is at Council Spending, which lists all individual payments over £250. The spending tables reveal projects few people outside the council have ever heard of, and show trends in spending on, say, consultants and what work they are being used for.
Sadly, despite government instructions on openness, councils are making of use of data protection legislation to conceal the identity of commercial suppliers, often on spurious grounds such as “security” and the fact that the private sector doesn’t publish such information. This policy – and it is a policy rather than a legal requirement – is being challenged locally and we will report further on this.
 Exeter City Council press and public exclusion notice
Exeter City Council press and public exclusion notice
Redacting information in the spending tables is just one technique councils use to keep information to themselves. Putting sensitive matters in “Part 2” of a meeting agenda enables councillors to exclude the press and public, then present a sanitised summary of the outcome in the published minutes.
Holding closed meetings is clearly desirable when staffing and organisation issues are being discussed; it is much less so when decisions on major spending and business plans are being taken.
The Information Commissioner upheld a complaint by this author that Exeter City Council were wrong to conceal the original business plan for the leisure centre now being built on the bus station site, though the council appealed to the Information Tribunal and all parties eventually agreed to stay the proceedings, not least because the original plan was overtaken by events.
There are other techniques for keeping information away from prying eyes. One of the most effective is to bypass the rules requiring meetings to take place in public by holding the discussion in a “working group” or other informal body. The Greater Exeter Visioning Board, which laid the groundwork for the slowly emerging Greater Exeter Strategic Plan, was not a formal committee of any of the councils involved and so was able to meet in private with impunity.
The same is true of the successor arrangements for oversight of developing the plan itself. Exeter City Council has a mysterious Planning Member Working Group described as a “sounding board” of members, which meets in private to discuss planning-related issues.
Then there is the simple “no, you can’t see it” tactic. The external review of community grants has been subject to that treatment, and one can only speculate what is in there that the council desperately wants to keep hidden. The same suspicions arise wherever something is withheld for no evident reason.
Yet information is important. Used openly and honestly, it is one of the key commodities that can help rebuild trust in our public institutions. We need to know not only what our representatives have decided, but how and why.
Citizens have remedies, developed in a less paranoid age. These include lobbying opposition councillors, asking questions at scrutiny committees, and making requests under the Freedom of Information Act. We will review these in detail in a further article.